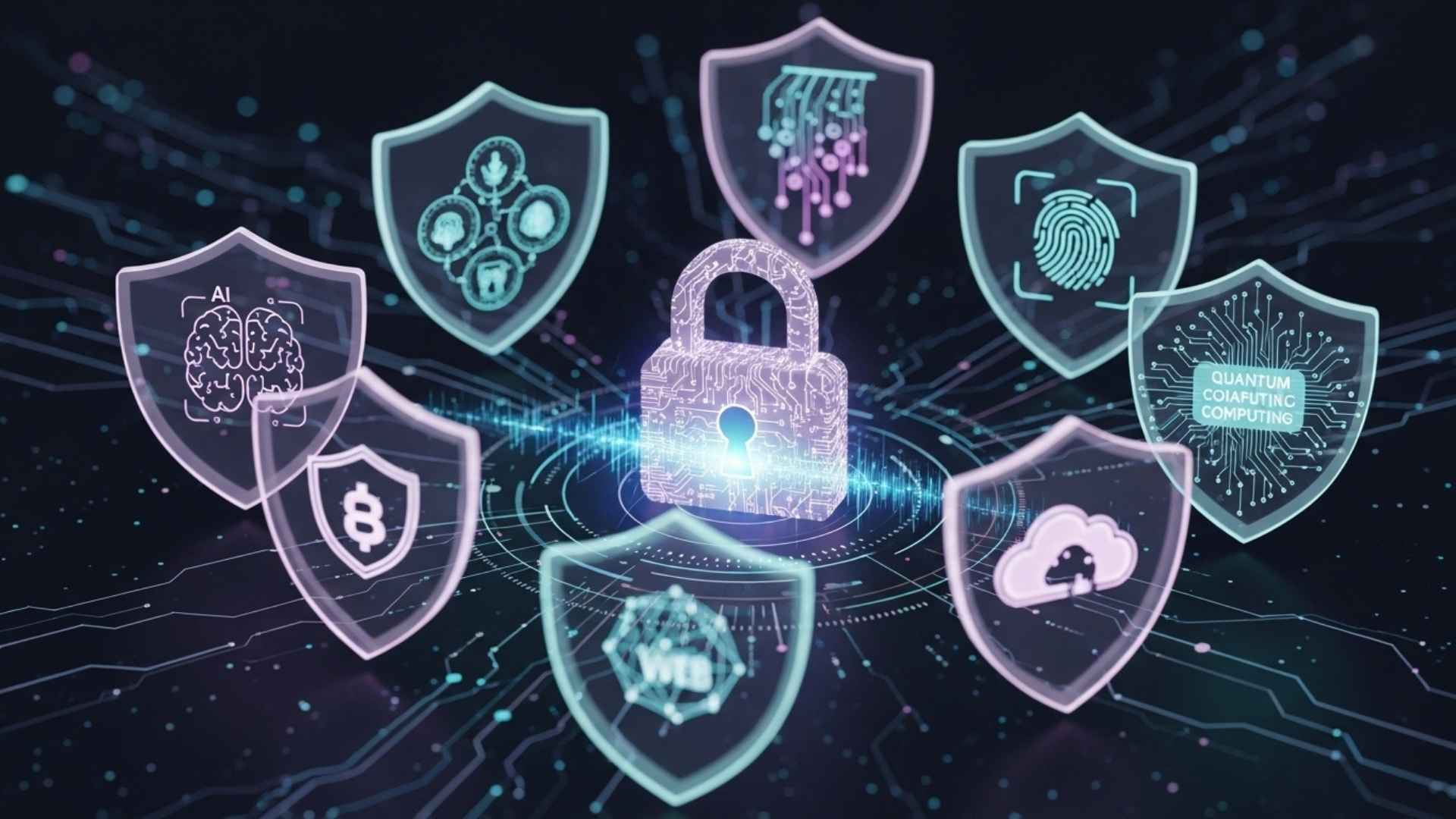
Cyberattacks will continue to increase in frequency and scale in 2025, and 2026 is unlikely to be a distant memory.
Emerging technologies such as Agentic AI and Quantum Computing are creating new opportunities for both good and bad. But as always, we humans are the weakest link and the strongest defense.
Experts predict that by 2026, if cybercrime were a country, it would be the third largest economy in the world, behind the United States and China, costing businesses an estimated $20 trillion. So, we look at the key trends that will drive this record-breaking global crime wave over the next 12 months.
1. Agentic AI Attacks and Defenses: A New Battlefield
AI Agents are becoming the new frontline in the fight against cybercrime.
As these systems operate autonomously and connect to external services, attackers will be able to launch more sophisticated attacks. They will be able to test defenses to find vulnerabilities and launch increasingly sophisticated social engineering and deception attacks.
But these AI Agents also offer powerful new options for defenses to automatically detect and respond.
So in 2026, these systems will push the cybersecurity arms race to the next level, increasing the threat level for both criminals and businesses.
2. Deepfake Fraud: Attacks with Fake Audio and Images
Deepfake technology has created new opportunities for attackers to impersonate trusted individuals and gain access to secure systems.
These incidents are already happening. There have been cases where employees have been tricked into transferring large amounts of money after receiving fake voice calls from their superiors.
As technology becomes more sophisticated and harder to distinguish from reality, these types of scams will only become more common.
3. Ransomware Threat: The Rise of Modern Extortion
Ransomware attacks continue to increase, and will become more sophisticated in 2026, after stealing and destroying critical business data.
Now, with the increasing availability of tools such as Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS), even less technically skilled criminals can begin to carry out these attacks. Deepfake technology also makes it easier to bypass human defenses.
In addition, the emergence of new, anonymous cryptocurrencies (digital currencies) allows criminals to easily transfer, launder, and spend the proceeds of the attacks without fear of punishment.
4. Humans: Strengthening the Weakest Link
The weakest link in security systems is usually humans.
Rather than breaking down innovative technological security barriers, criminals are finding it easier to trick, bribe, or coerce people into revealing access credentials.
In response, businesses will invest more in training their employees to understand threats, conducting systematic fake attacks using social engineering techniques, and building a culture of security awareness across the organization.
5. Quantum Security: The Threat to Encryption
Quantum computers will be able to solve problems in seconds that would take the most powerful computers hundreds of years to solve, and will undoubtedly transform science, health, and finance.
But this technology also poses a major threat to the encryption that protects sensitive information and communications. Criminals are already collecting vast amounts of data in advance of the time when quantum technology can read it.
The focus in 2026 will be on identifying vulnerabilities and transitioning to quantum-safe encryption systems before it’s too late.
6. Regulatory Reform: Legal Pressure
Regulators and lawmakers are still struggling to keep up with the rapid evolution of cybercrime.
This change is not about punishing criminals (they don’t obey the law), but about pressuring companies to protect valuable customer data.
The US SEC’s new cyber disclosure rules will force companies to report and document data breaches. At the same time, the European Union’s NIS2 directive will expand the obligation for businesses to implement security measures.
Whether these measures will help stop the wave of data theft and extortion in 2026 remains to be seen.
How do you think these regulatory changes will change the way businesses do business?
7. Cyberwarfare on the World Stage
As the war in Ukraine has shown, cyberattacks and disinformation campaigns targeting critical infrastructure, communications networks, and supply chains are now everyday weapons of war.
State-sponsored and terrorist-organized attacks are attacking energy and healthcare systems, disrupting businesses, and creating economic instability. Deepfake technology is also being widely used to embarrass politicians and undermine trust in the democratic process.
In 2026, cybercrime will no longer just threaten individual privacy and business finances. It has become a major national security threat.
To counter this threat, we will see governments increase spending on cyber defense and research, and form new alliances.
Also Read: What is an AI Assistant? Key Facts You Need to Know
Prepare Now: There’s No Time to Delay
The cybersecurity landscape of 2026 represents a truly pivotal moment. Emerging technologies are both increasing the capabilities of criminals and increasing the opportunities for defense.
While the scale of the threat can be daunting at times, organizations that invest in quantum-safe encryption, AI-powered defenses, and human training will be in the best position to survive and thrive.
The key takeaway here is that now is the time to act before criminals gain a greater advantage.